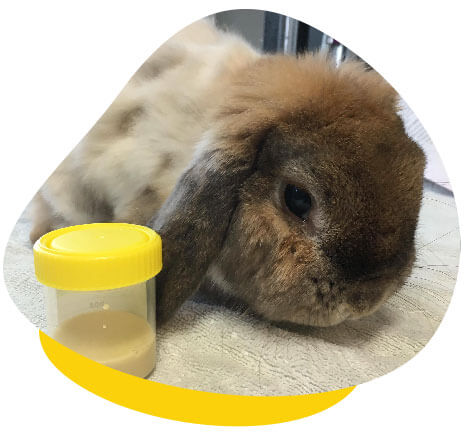
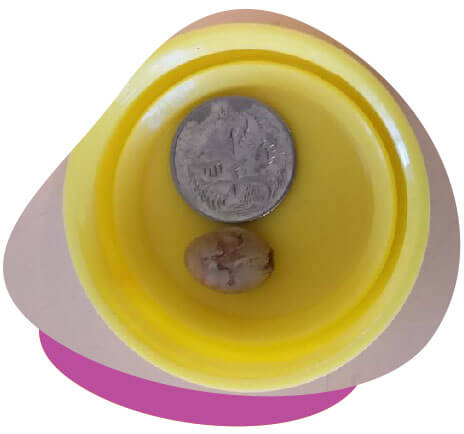
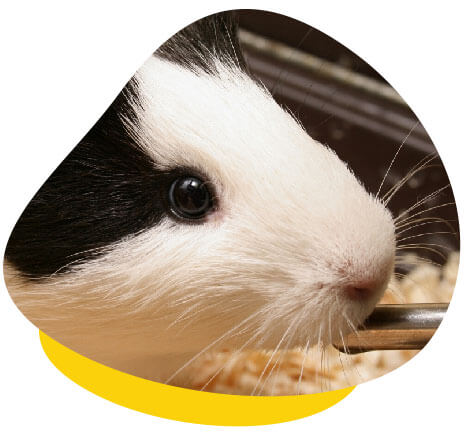
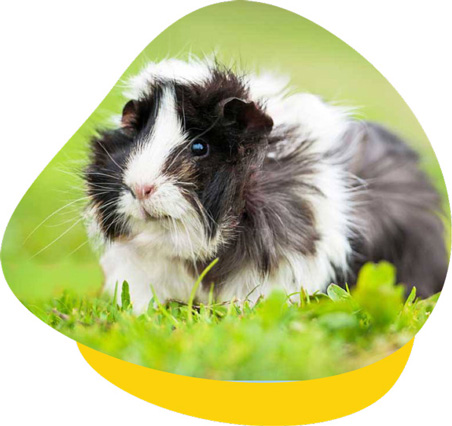
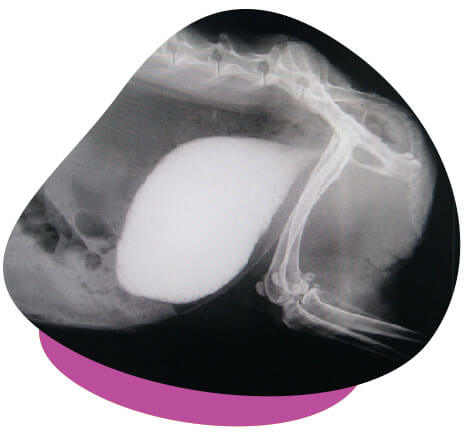
Urinary problems are common in guinea pigs and rabbits, frequently manifesting as the formation of uroliths (also known as ‘urinary stones’) and the presence of urinary sludge. These conditions arise when an excess of calcium accumulates in the urinary tract, posing a potential health risk for these small animals.
Urinary sludge, characterised by dense calcium crystals, resembles toothpaste in texture and often proves challenging to eliminate completely through normal urination. Typically, the sludge settles at the bottom of the bladder, with regular urine on top. This gritty, grey paste gets expelled only during the final stages of urination.